Fast & Accurate ENS GB & EU ICS2 Solutions Built for You.
10 Steps to Achieve Customs Compliance
-
Freya Jane
- Director of Customer's Success
In today’s global marketplace, navigating customs compliance is just one of the many hurdles businesses encounter in international trade. To glide smoothly across borders, dodge fines, and uphold a stellar reputation, honouring customs guidelines is a must.
In the realm of global trade, customs rules are unavoidable. Slip-ups could mean delays, penalties, and a dent in your credibility. We’ve put together ten crucial steps any business can adopt to simplify operations and meet customs demands, ensuring happy customers and a thriving business.
What is customs compliance?
Customs compliance is adhering to the guidelines from the relevant governments and customs authorities set forth for international trade. It requires ensuring that all shipments entering and leaving the country meet local customs requirements. Accurate paperwork, correct categorisation and value of commodities, and observance of imports.
Export regulations, enforcement of rules of origin, and maintaining transaction records are some aspects of business that fall within customs compliance. It allows firms to avoid fines and delays, lessen risk exposure, protect their good name, and succeed in the competitive global marketplace.
It allows companies to make the most of advantageous trade deals and streamline supply chain operations. Businesses can’t function internationally lawfully and profitably if they violate customs regulations.
Learn more about customs compliance with the detailed guide. Read here!
Why is customs compliance substantial?
Compliance with customs regulations is of the utmost significance for firms that are involved in international commerce for the following reasons:
1.1. Border operations:
Customs rules facilitate cross-border trade. Businesses may prevent delays, customs clearance, and supply chain interruptions by fulfilling all regulations and following processes..
1.2. Legality and penalties
Customs violations may lead to fines, forfeiture, and legal action. Businesses show their dedication to legality and avoid expensive fines by obtaining customs compliance.
1.3. Reputation and trust
Adherence to trade rules enhances a company’s reputation as a trustworthy trading partner. It’s all about building confidence with consumers, suppliers, and customs authorities by demonstrating integrity, ethical behaviour, and remaining on the right side of the law.
1.4. Risk mitigation
Customs compliance reduces international commerce risks such as misclassification, value problems, import/export restrictions, and trade penalties. Businesses may avoid customs audits, delays, legal concerns, and brand harm by managing compliance.
1.5. Trade advantages
Companies that comply with customs regulations are eligible for tariff reductions and other benefits of preferential trade agreements. This comprises duty-free trade zones, reduced customs duties, and trusted trader programmes that expedite customs processes and trade facilitation.
1.6. Logistics efficiency
By facilitating customs clearance, international trade compliance enhances supply chain efficiency, lead times, inventory management, and operational efficiency.
1.7. Trade compliance incentive programmes
1.8. Data precision
Customs laws require proper data collection and reporting. Better trade data benefits market research, supply chain optimisation, and regulatory reporting.
Feeling burdened by the complexities of customs compliance?
Automate tasks, minimise errors, and ensure compliance with iCustoms!
Advantages and disadvantages of customs compliance
Process automation and robotic automation are two different terms or advancements that vary by company. Robotics and process automation streamline and optimise business operations. Both have important differences:
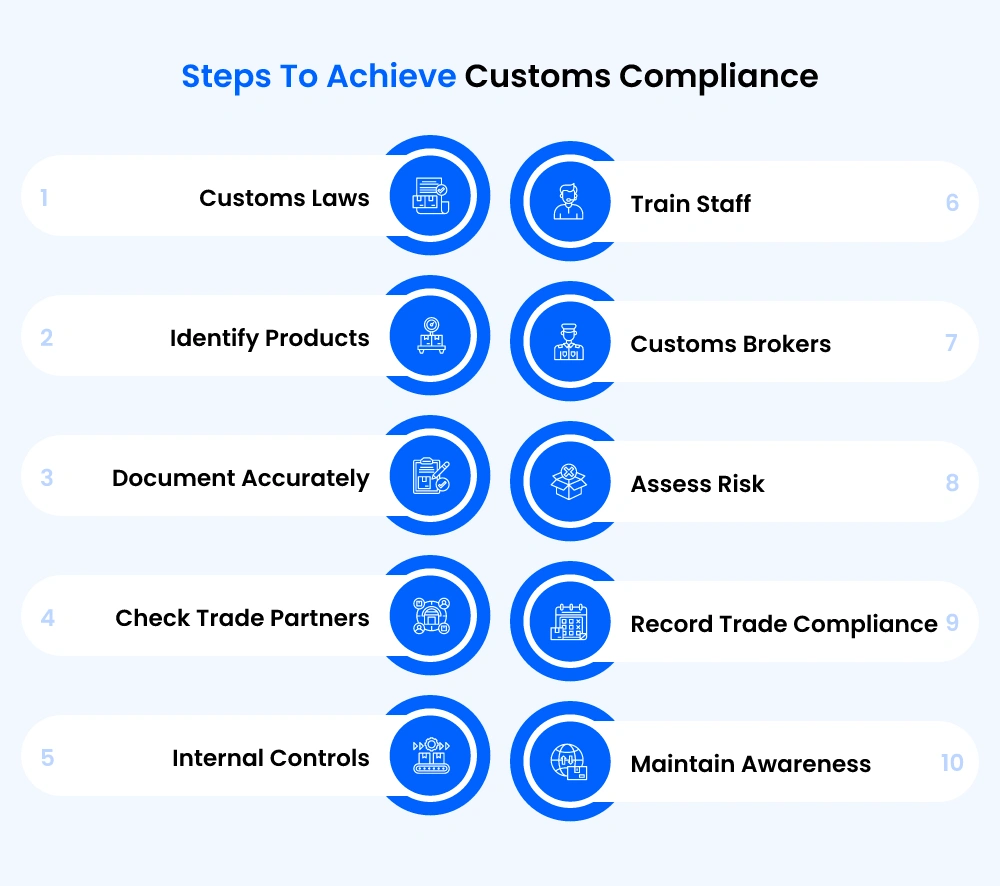
Ten steps to achieve customs compliance in 2024
1. Customs laws
Learn everything about the customs laws of the nations you’ll work with. Learn about the necessary paperwork, methods of valuation, and constraints associated with importing and exporting.
2. Identify products
Make sure you’re using the correct HS codes when categorising your items. The right customs charges, taxes, import/export restrictions, or licensing requirements may only be calculated with accurate categorisation.
3. Document accurately
Documentation such as invoices, packing lists, shipping documentation, and customs declarations are all part of the import/export process and should be kept in a thorough record. Make sure that anything that customs officials or auditors could need is readily available, accurate, and comprehensive.
4. Check trade partners
You should investigate your business partners, suppliers, customers, and logistical service providers. Ensure they have a good reputation, follow the rules for customs, and operate ethically.
5. Internal controls
Put in place safeguards and protocols to guarantee that all customs laws are followed. Compliance gaps may be fixed by defining roles and responsibilities, separating tasks, putting checks and balances in place, and performing frequent internal audits.
6. Train staff
Employees who handle imports and exports should get consistent training and instruction. Provide them with the information they need to comprehend customs laws, paperwork norms, compliance protocols, and any changes to the customs environment.
7. Customs brokers
If you need assistance meeting customs standards, completing paperwork, or figuring out how to proceed, hire a customs broker or consultant.
8. Assess risk
Keep an eye out for compliance issues and supply chain weaknesses by conducting regular risk assessments. Considerations such as product categorisation, determining the country of origin, valuation methodologies, and compliance with trade restrictions or embargoes are evaluated.
9. Record trade compliance
Documentation, audit reports, and remedial actions should all be part of your compliance records. This is proof of your efforts and shows that you care about following customs regulations.
10. Maintain awareness
Keep up with the ever-evolving customs rules, trade pacts, and tariffs. To keep up with the ever-changing customs regulations, consult authoritative sources, including customs officials, industry magazines, trade groups, and related seminars and workshops.
Save time, reduce errors, and ensure compliance with iCDS. Start Now!
Conclusion
Businesses may confidently manage the difficulties of international commerce by adhering to these 10 essential measures for customs compliance. A reliable and efficient global supply chain can only be fostered when firms adhere to customs requirements, keep correct records, and establish strong compliance practices to prevent expensive fines and delays.
FAQ's
What is customs and trade compliance?
Customs and trade compliance is adhering to the regulations and laws that control imports, exports, and international trade in order to assure legal and ethical business practices.
What are the pillars of customs compliance?
Customs compliance pillars include proper documentation, value, classification, country of origin, and duty and tax payment—all of which are necessary to comply with customs requirements.
How does valuation impact customs compliance?
Valuation, or estimating the value of items for customs purposes, assures proper duty calculation and conformance to customs regulations, which is a critical component of compliance.
How does tariff classification impact customs compliance?
Tariff classification assigns classifications to commodities, which are necessary for tariff calculation and regulatory compliance, as well as accurate declaration and clearance at customs checkpoints.
You may also like:
Empower Your Business with Smart Declaration Software
Enhance Efficiency, Reduce Errors, & Simplify Customs Management
Subscribe to our Newsletter
About iCustoms
Empower Your Business with Smart Declaration Software
Enhance Efficiency, Reduce Errors, & Simplify Customs Management

